Structural mechanism of bridge RNA-guided recombination
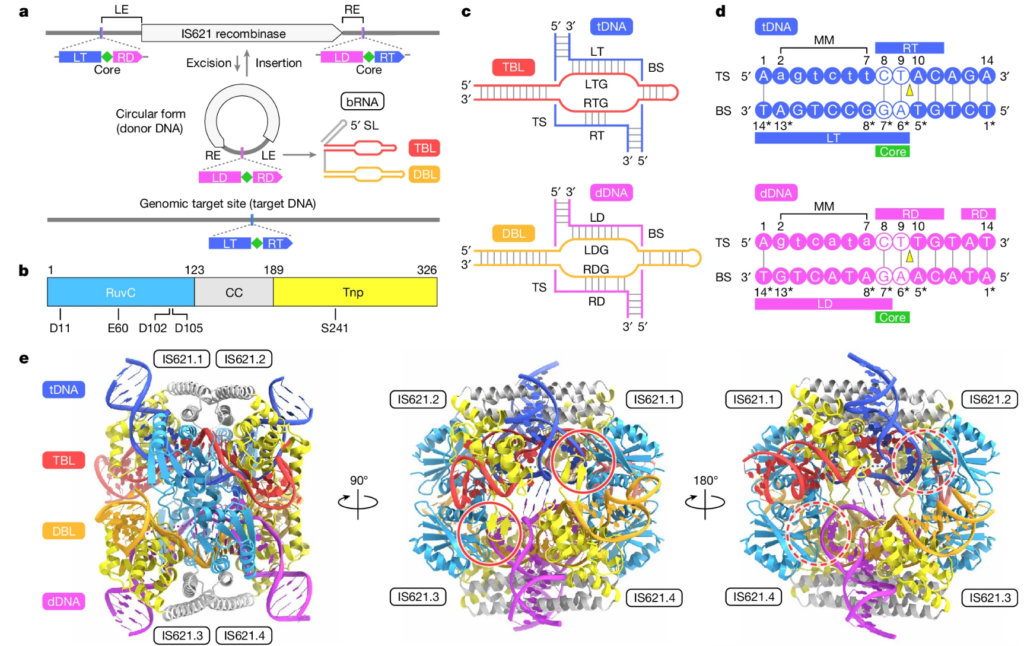
挿入配列(IS)は、原核生物のゲノムに見られる最も単純な自律的転移因子である。我々は最近、IS110ファミリー配列が、リコンビナーゼと、2つのプログラム可能なループによりターゲットDNAとドナーDNAに対する特異性を与える非翻訳ブリッジRNA(bRNA)をコードしていることを見いだした。今回我々は、組換え反応サイクルの3つの異なる段階において、bRNAやターゲットDNA、ドナーDNAと複合体を形成したIS110リコンビナーゼのクライオ電子顕微鏡構造を報告する。IS110接合複合体は、2つのリコンビナーゼ二量体から構成され、一方はbRNAのターゲット結合ループを収納しターゲットDNAと結合するのに対し、もう一方はbRNAのドナー結合ループとドナーDNAと結合していた。我々は、ターゲットDNAおよびドナーDNAの両方の組換え部位の近くに触媒セリン残基が配置されたRuvC-Tnp複合活性部位が2つの二量体の間に形成されることを明らかにした。3つの構造の比較から、(1)ターゲットDNAとドナーDNAのトップ鎖が複合活性部位で切断され、5′-ホスホセリン共有結合中間体が形成されること、(2)切断されたDNA鎖が交換、再連結しホリデイ構造中間体が形成されること、(3)その後、この中間体がボトム鎖の切断により解消されることが明らかになった。総合すると、この研究により、プログラム可能なDNA組換えのために、二重特異的なRNAがターゲットDNAおよびドナーDNAに対する特異性をIS110リコンビナーゼに与える機構が明らかになった。
Insertion sequence (IS) elements are the simplest autonomous transposable elements found in prokaryotic genomes. We recently discovered that IS110 family elements encode a recombinase and a non-coding bridge RNA (bRNA) that confers modular specificity for target DNA and donor DNA through two programmable loops. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of the IS110 recombinase in complex with its bRNA, target DNA and donor DNA in three different stages of the recombination reaction cycle. The IS110 synaptic complex comprises two recombinase dimers, one of which houses the target-binding loop of the bRNA and binds to target DNA, whereas the other coordinates the bRNA donor-binding loop and donor DNA. We uncovered the formation of a composite RuvC–Tnp active site that spans the two dimers, positioning the catalytic serine residues adjacent to the recombination sites in both target and donor DNA. A comparison of the three structures revealed that (1) the top strands of target and donor DNA are cleaved at the composite active sites to form covalent 5′-phosphoserine intermediates, (2) the cleaved DNA strands are exchanged and religated to create a Holliday junction intermediate, and (3) this intermediate is subsequently resolved by cleavage of the bottom strands. Overall, this study reveals the mechanism by which a bispecific RNA confers target and donor DNA specificity to IS110 recombinases for programmable DNA recombination.
Authors: Masahiro Hiraizumi, Nicholas T. Perry, Matthew G. Durrant, Teppei Soma, Naoto Nagahata, Sae Okazaki, Januka S. Athukoralage, Yukari Isayama, James J. Pai, April Pawluk, Silvana Konermann, Keitaro Yamashita, Patrick D. Hsu, Hiroshi Nishimasu
Journal: Nature 630, 994–1002 (2024)
Press Release: https://www.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ja/news/release/20240627.html
投稿者プロフィール