Bridge RNAs direct programmable recombination of target and donor DNA
ゲノムの再編成は、挿入や欠失、逆位といった変異につながる変化を含め、遺伝的多様性に重要な役割を果たす。このようなゲノム再編成は通常、相同組換えのような基本的なDNA修復過程に関わる酵素や、ウイルスや可動性遺伝因子による外来遺伝物質の転位に関わる酵素によって行われる。今回我々は、小型自律的可動性遺伝因子ファミリーであるIS110挿入配列が、自身がコードするリコンビナーゼに特異的に結合する構造化された非翻訳RNAを発現していることを明らかにした。このブリッジRNAは2つの内部ループを含み、そこにはターゲットDNAやドナーDNA(IS110因子そのもの)と塩基対形成するヌクレオチド配列がコードされている。このターゲット結合ループとドナー結合ループの配列はそれぞれ独自にリプログラムすることが可能であり、それにより2分子のDNA間で配列特異的な組換えを引き起こせることが実証された。このモジュラー性のため、ゲノムの標的部位へのDNA挿入やプログラム可能なDNA切除、反転が可能である。このIS110ブリッジ組換えシステムは、核酸ガイドシステムの多様性をCRISPRやRNA干渉を越えて拡大するもので、ゲノムデザインに必要な挿入、切除、反転という3つの基本的なDNA再編成のための統一的方法を提供する。
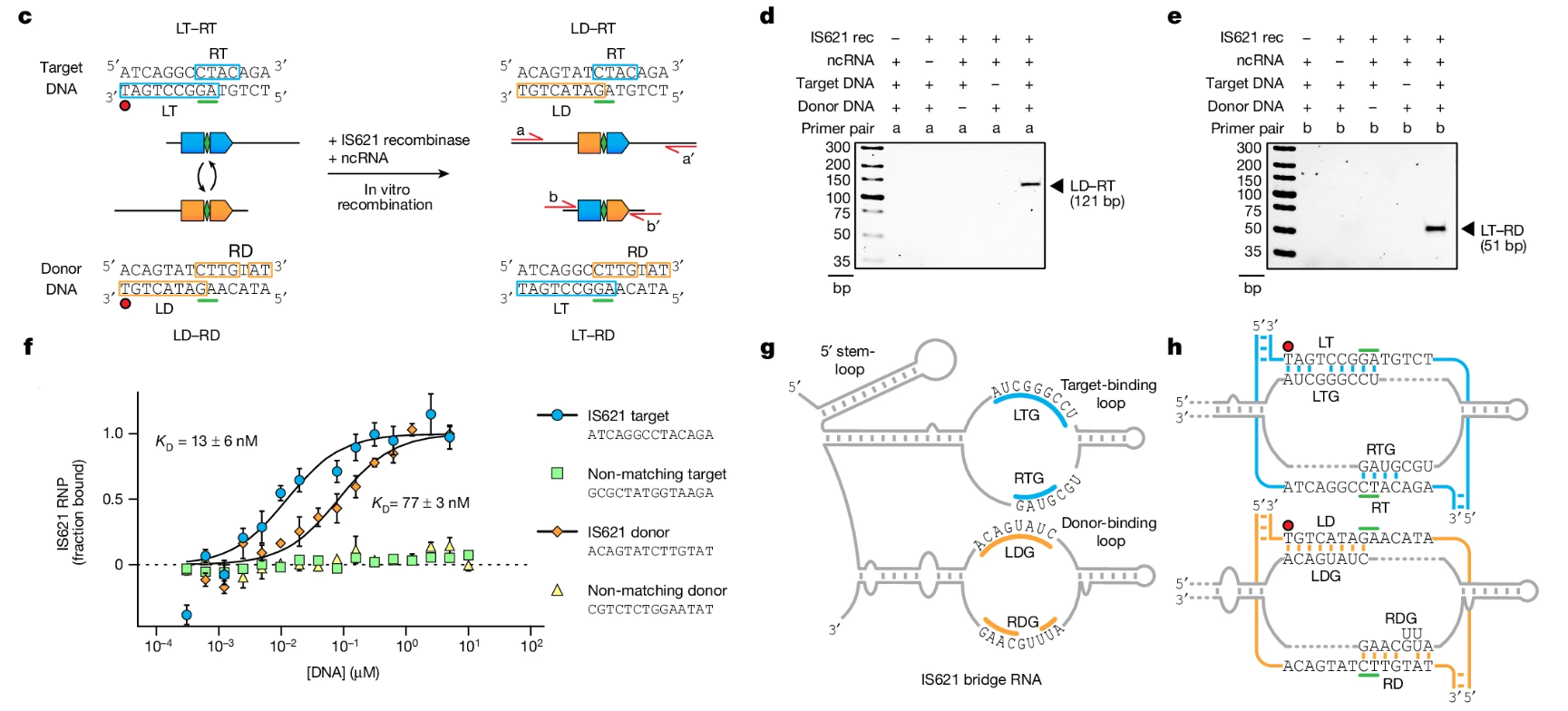
Genomic rearrangements, encompassing mutational changes in the genome such as insertions, deletions or inversions, are essential for genetic diversity. These rearrangements are typically orchestrated by enzymes that are involved in fundamental DNA repair processes, such as homologous recombination, or in the transposition of foreign genetic material by viruses and mobile genetic elements. Here we report that IS110 insertion sequences, a family of minimal and autonomous mobile genetic elements, express a structured non-coding RNA that binds specifically to their encoded recombinase. This bridge RNA contains two internal loops encoding nucleotide stretches that base-pair with the target DNA and the donor DNA, which is the IS110 element itself. We demonstrate that the target-binding and donor-binding loops can be independently reprogrammed to direct sequence-specific recombination between two DNA molecules. This modularity enables the insertion of DNA into genomic target sites, as well as programmable DNA excision and inversion. The IS110 bridge recombination system expands the diversity of nucleic-acid-guided systems beyond CRISPR and RNA interference, offering a unified mechanism for the three fundamental DNA rearrangements—insertion, excision and inversion—that are required for genome design.
Authors: Matthew G. Durrant, Nicholas T. Perry, James J. Pai, Aditya R. Jangid, Januka S. Athukoralage, Masahiro Hiraizumi, John P. McSpedon, April Pawluk, Hiroshi Nishimasu, Silvana Konermann, Patrick D. Hsu
Journal: Nature 630, 984–993 (2024)
Press Release: https://www.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ja/news/release/20240627.html
投稿者プロフィール